马上注册,结交更多好友,享用更多功能,让你轻松玩转社区。
您需要 登录 才可以下载或查看,没有账号?立即注册
×
《Fuel Cells: Principles, Design, and Analysis》
燃料电池:原理、设计和分析
作者: Shripad T. Revankar, Pradip Majumdar
出版社:CRC
出版时间:2014年
《Fuel Cells: Principles, Design, and Analysis》

《Fuel Cells: Principles, Design, and Analysis》

《Fuel Cells: Principles, Design, and Analysis》

目录
Preface.................................................................................................................... xxi
Acknowledgments.............................................................................................. xxv
Authors...............................................................................................................xxvii
1. Introduction......................................................................................................1
1.1 Primary Energy Sources—Fossil Fuel................................................1
1.1.1 Coal.............................................................................................2
1.1.2 Liquid or Gaseous Hydrocarbons..........................................2
1.1.3 World Oil Reserve.....................................................................4
1.1.4 Shale Oil.....................................................................................4
1.1.5 Gaseous Hydrocarbons............................................................5
1.1.6 Shale Gas....................................................................................5
1.1.7 Biofuel.........................................................................................5
1.1.7.1 Challenges of Ethanol—Biofuel..............................5
1.2 Renewable Energy Resources and Alternative Energy Systems.....6
1.2.1 Solar Energy..............................................................................7
1.2.2 Tidal Energy..............................................................................7
1.2.3 Geothermal Energy..................................................................7
1.2.4 Wind Energy..............................................................................7
1.2.5 Renewable Energy for Hydrogen Production......................7
1.2.6 Hydrogen Production and Hydrogen Fuel Cell...................8
1.3 Electrochemical Device—Basic Components and Operation.........8
1.3.1 Electrolyzer.............................................................................. 10
1.3.2 Battery...................................................................................... 10
1.3.2.1 Battery Technology................................................. 14
1.3.3 Fuel Cell.................................................................................... 15
1.4 Basic Components and Operation of a Fuel Cell............................. 15
1.5 Classification and Types of Fuel Cell................................................ 17
1.5.1 Alkaline Fuel Cell................................................................... 19
1.5.2 Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell................................20
1.5.3 Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cell..................................................... 21
1.5.4 Molten Carbonate Fuel Cell................................................... 21
1.5.5 Solid Oxide Fuel Cell..............................................................22
1.5.6 Direct Methanol Fuel Cell.....................................................23
1.5.7 Micro Fuel Cells......................................................................23
1.5.8 Biological Fuel Cells............................................................... 24
1.5.8.1 Microbial Biofuel Cells...........................................25
1.5.8.2 Enzymatic Biofuel Cell...........................................26
x Contents
1.6 Applications of Fuel Cell.....................................................................28
1.6.1 Transportation.........................................................................28
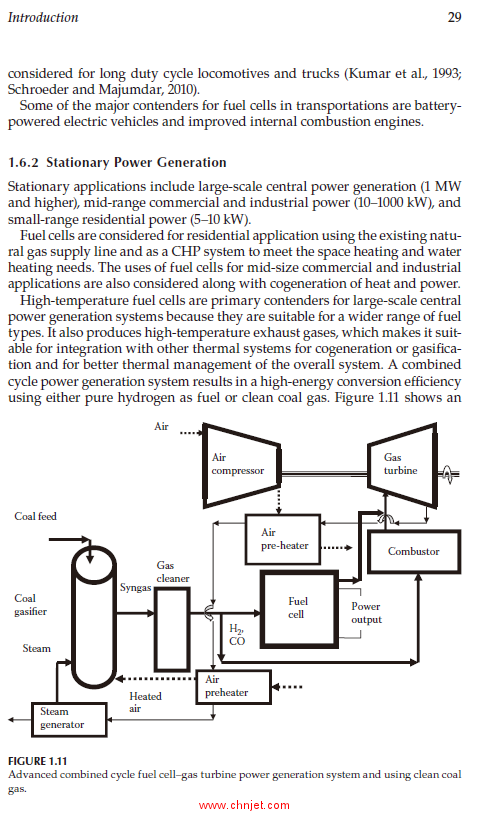
1.6.2 Stationary Power Generation................................................29
1.6.3 Portable Power.........................................................................30
References........................................................................................................30
2. Review of Electrochemistry........................................................................33
2.1 Electrochemical and Electrolysis Cell...............................................36
2.2 Oxidation and Reduction Processes..................................................40
2.3 Faraday’s Laws.....................................................................................42
2.3.1 Faraday’s First Law of Electrolysis.......................................43
2.3.2 Faraday’s Second Law of Electrolysis..................................43
2.4 Ideal Polarized Electrode....................................................................45
2.5 Polarization and Overpotential.........................................................46
2.6 Conductivity and Ohm’s Law............................................................47
2.7 Mass Transport and Nernst–Planck Equation.................................49
2.8 Standard Hydrogen and Other Reference Electrodes.................... 51
2.8.1 Standard Hydrogen Electrode and Potentials.................... 51
2.8.2 Reference Electrodes..............................................................54
2.9 Cyclic Voltammetry.............................................................................54
References........................................................................................................58
3. Reviews of Thermodynamics..................................................................... 59
3.1 State, Phase, and Properties................................................................ 59
3.2 Thermodynamic Process and Cycle..................................................60
3.3 Ideal Gas Equation of State................................................................. 61
3.4 Energy and Energy Transfer.............................................................. 62
3.4.1 Heat and Work........................................................................63
3.4.1.1 Heat Energy.............................................................63
3.4.1.2 Work..........................................................................63
3.5 The Conservation of Mass..................................................................64
3.5.1 System.......................................................................................64
3.5.2 Control Volume.......................................................................65
3.6 The First Law of Thermodynamics...................................................65
3.6.1 The First Law of Thermodynamics for a System...............65
3.6.1.1 Additional Thermodynamic Properties..............66
3.6.2 The First Law of Thermodynamics for a Control
Volume...................................................................................... 67
3.6.2.1 Special Cases............................................................ 67
3.6.2.2 Steady-State Steady-Flow Process.........................68
3.6.2.3 Uniform-Flow Uniform-State Process..................68
3.7 The Second Law of Thermodynamics.............................................. 69
3.7.1 Carnot Cycle............................................................................71
3.8 Thermodynamic Relations.................................................................73
3.9 Specific Heat......................................................................................... 74
Contents xi
3.10 Estimation of Change in Enthalpy, Entropy, and Gibbs
Function for Ideal Gases..................................................................... 74
3.10.1 Case I: Constant Specific Heat..............................................75
3.10.2 Case II: Temperature-Dependent Specific Heat
Values............................................................................... 75
3.10.3 Case III......................................................................................75
3.10.4 Entropy Change in Process................................................... 76
3.10.5 Special Cases........................................................................... 76
3.10.5.1 Case I: Constant Specific Heat Values.................. 76
3.10.5.2 Case II: Temperature-Dependent Specific
Heat Values............................................................... 76
3.10.5.3 Case III......................................................................77
3.10.6 Change of Gibbs Function.....................................................77
3.11 Mixture of Gases..................................................................................79
3.11.1 Basic Mixture Parameters......................................................79
3.11.1.1 Mass Fraction and Concentration.........................80
3.11.1.2 Mole Fraction and Concentration.........................80
3.11.2 Ideal Gas Mixture Properties................................................ 81
3.11.3 Transport Properties of Gas Mixture...................................84
3.11.3.1 Viscosity of Gas Mixture........................................84
3.11.3.2 Thermal Conductivity of Gas Mixture................85
3.12 Combustion Process............................................................................86
3.13 Enthalpy of Formation hf
( 0 )...............................................................90
3.14 First Law for Reacting Systems.......................................................... 91
3.15 Enthalpy of Combustion (hRP)............................................................92
3.16 Temperature of Product of Combustion...........................................93
3.17 Absolute Entropy sf
( 0 )........................................................................97
3.18 Gibbs Function of Formation gf
( 0 ).....................................................98
References...................................................................................................... 102
4. Thermodynamics of Fuel Cells................................................................. 103
4.1 Conventional Power Generation—Heat Engine............................ 103
4.2 Energy Conversion in Fuel Cells..................................................... 107
4.2.1 Electrical Work in Fuel Cells............................................... 112
4.2.2 Reversible Cell Voltage......................................................... 113
4.2.3 Cell Power.............................................................................. 114
4.3 Changes in Gibbs Free Energy......................................................... 115
4.4 Effect of Operating Conditions on Reversible Voltage................. 121
4.4.1 Effect of Variation of Temperature.....................................122
4.4.2 Effect of Pressure on Gibbs Function and Reversible
Voltage....................................................................................122
4.4.3 Effect of Gas Concentration—The Nernst Equation........ 124
4.4.3.1 Effect of Hydrogen Partial Pressure................... 128
4.4.3.2 Effect of Oxygen Partial Pressure....................... 129
xii Contents
4.5 Fuel Cell Efficiency............................................................................ 133
4.5.1 Thermodynamic Efficiency................................................. 134
4.5.2 Voltage Efficiency.................................................................. 136
4.5.3 Current or Fuel Utilization Efficiency................................ 137
4.5.4 Overall Efficiency.................................................................. 138
4.6 Fuel Consumption and Supply Rates.............................................. 138
4.6.1 Oxygen Consumption and Supply Rates.......................... 138
4.6.1.1 Direct Oxygen Consumption.............................. 139
4.6.1.2 Oxygen Consumption as Air............................... 140
4.6.2 Hydrogen Consumption and Supply Rates...................... 141
4.7 Water Production Rate...................................................................... 142
4.8 Heat Generation in a Fuel Cell......................................................... 143
4.8.1 Heat Generation owing to Electrochemical Reaction...... 144
4.8.2 Heat Generation owing to Non-Electrochemical
Reaction.................................................................................. 147
4.8.3 Total Heat Generation in a Fuel Cell.................................. 148
4.9 Summary............................................................................................. 152
References...................................................................................................... 154
5. Electrochemical Kinetics............................................................................ 155
5.1 Electrical Double Layer..................................................................... 155
5.2 Electrode Kinetics.............................................................................. 162
5.3 Single- and Multistep Electrode Reactions.................................... 166
5.4 Electrode Reaction in Equilibrium—Exchange Current
Density................................................................................................. 173
5.5 Equation for Current Density—The Butler–Volmer
Equation................................................................................... 176
5.6 Activation Overpotential and Controlling Factors....................... 178
5.7 Tafel Equation—Simplified Activation Kinetics........................... 180
5.8 Relationship of Activation Overpotential with Current
Density—Tafel Plots........................................................................... 186
5.9 Fuel Cell Kinetics............................................................................... 188
5.10 Fuel Cell Irreversibilities—Voltage Losses..................................... 191
5.10.1 Activation Losses.................................................................. 194
5.10.2 Ohmic Losses........................................................................ 196
5.10.3 Mass Transport Loss............................................................ 199
5.10.4 Reactant Crossover and Internal Currents........................205
5.11 Fuel Cell Polarization Curve............................................................209
5.12 Summary............................................................................................. 213
References...................................................................................................... 214
6. Heat and Mass Transfer in Fuel Cells..................................................... 215
6.1 Fluid Flow........................................................................................... 215
6.1.1 External Flow........................................................................ 216
6.1.2 Internal Flows........................................................................ 218
Contents xiii
6.1.3 Gas Flow Channels...............................................................220
6.1.3.1 Conservation of Mass...........................................220
6.1.3.2 Conservation of Momentum............................... 221
6.1.4 Fluid Flow in Porous Electrodes.........................................222
6.1.4.1 Mass Continuity in Porous Media......................222
6.1.4.2 Momentum Equation in Porous Media.............223
6.1.5 Inlet and Boundary Conditions..........................................225
6.1.5.1 Inlet Conditions.....................................................225
6.1.5.2 Boundary Conditions...........................................226
6.2 Heat Transfer in Fuel Cells...............................................................226
6.2.1 Heat Transfer Modes and Rate Equations.........................228
6.2.1.1 Conduction Heat Transfer....................................228
6.2.1.2 Convection Heat Transfer....................................229
6.2.2 Convection Modes and Heat Transfer Coefficient........... 231
6.2.2.1 Fully Developed Correlations.............................233
6.2.2.2 Thermal Entry Length..........................................233
6.2.2.3 Combined Entry Length......................................233
6.2.3 Conservation of Energy and Heat Equation.....................234
6.2.3.1 Gas Flow Channel.................................................234
6.2.3.2 Electrode–Gas Diffusion Layer...........................235
6.2.3.3 Electrolyte Membrane..........................................235
6.2.4 Inlet and Boundary Conditions..........................................235
6.2.4.1 Boundary Conditions...........................................235
6.2.4.2 Channel Inlet Conditions.....................................236
6.3 Mass Transfer in Fuel Cells.............................................................. 237
6.3.1 Basic Modes and Transport Rate Equation.......................238
6.3.1.1 Diffusion Mass Transfer.......................................238
6.3.1.2 Convection Mass Transfer.................................... 241
6.3.1.3 Combined Diffusion and Convection Mass
Transport................................................................ 243
6.3.2 Mass Species Transport in Fuel Cells................................ 244
6.3.2.1 Mass Species Transport Equation in Gas
Flow Channels....................................................... 244
6.3.2.2 Mass Species Transport Equation in
Electrodes............................................................... 245
6.3.2.3 Boundary Conditions for Concentration........... 247
6.3.2.4 Channel Inlet Conditions..................................... 247
6.3.3 Convection Mass Transfer Coefficient............................... 249
6.3.3.1 Mass Transfer Resistances...................................253
6.3.3.2 Concentration Distribution in the Active
Reaction Layer....................................................... 257
6.4 Diffusion Coefficient......................................................................... 257
6.4.1 Diffusion Coefficient for Binary Gas Mixture.................. 257
6.4.2 Diffusion in Liquids.............................................................264
6.4.3 Diffusion in Porous Solids................................................... 266
xiv Contents
6.5 Mass Transfer Resistance in Fuel Cells...........................................268
6.5.1 Estimation of Limiting Current Density........................... 269
6.5.2 Mass Transfer or Concentration Loss................................ 270
6.5.3 Effect of Concentration on Activation Loss...................... 272
6.6 Summary............................................................................................. 273
Further Reading............................................................................................ 274
7. Charge and Water Transport in Fuel Cells.............................................277
7.1 Charge Transport...............................................................................277
7.1.1 Charge Transport Modes and Rate Equations................. 278
7.1.1.1 Charge Transport by Diffusion........................... 278
7.1.1.2 Charge Transport by Convection........................ 278
7.1.1.3 Charge Transport by Electrical Potential
Gradient.................................................................. 279
7.1.1.4 Nernst–Planck’s Equation....................................280
7.1.1.5 Schlogl’s Equation................................................. 281
7.1.2 Charge Transport and Electrical Potential Equation....... 281
7.1.2.1 Charge Transport Equations...............................285
7.1.2.2 Boundary Conditions for Electrical Potential....287
7.1.3 Agglomerate Model for the Active Catalyst Layer...........288
7.2 Solid-State Diffusion.......................................................................... 291
7.3 Charge Conductivity......................................................................... 293
7.3.1 Ionic Conductivity (σi).......................................................... 294
7.3.1.1 Ionic Conductivity in Solid Electrolytes............ 296
7.3.1.2 Ionic Conductivity in Polymer Electrolyte
Membrane.............................................................. 296
7.3.1.3 Ionic Conductivity in Ceramic Electrolyte
Membrane.............................................................. 297
7.3.1.4 Ionic Conductivity in Liquid Electrolyte...........299
7.3.2 Electronic Conductivity (σe)................................................300
7.4 Ohmic Loss in Fuel Cells.................................................................. 301
7.5 Water Transport Rate Equation........................................................305
7.5.1 Water Transport in Electrolyte Membranes......................306
7.5.2 Water Transport Equation................................................... 310
7.6 Summary............................................................................................. 311
Further Reading............................................................................................ 312
8. Fuel Cell Characterization......................................................................... 315
8.1 Characterization of Fuel Cells and Fuel Cell Components.......... 315
8.2 Electrochemical Characterization Techniques.............................. 317
8.2.1 Current–Voltage Measurement........................................... 317
8.2.2 Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy....................... 320
8.2.2.1 Equivalent Circuit Models................................... 323
8.2.2.2 Constant Phase Element....................................... 324
Contents xv
8.2.2.3 Polarization Resistance......................................... 324
8.2.2.4 Charge Transfer Resistance................................. 325
8.2.2.5 Warburg Impedance............................................. 325
8.2.2.6 Fuel Cell Equivalent Circuit Modeling.............. 329
8.2.2.7 Time and Frequency Domains............................330
8.2.3 Current Interrupt Measurement......................................... 331
8.2.4 Cyclic Voltammetry..............................................................333
8.3 Characterization of Electrodes and Electrocatalysts....................334
8.4 Characterization of Membrane Electrode Assembly.................... 339
8.5 Characterization of Bipolar Plates...................................................343
8.6 Characterization of Porous Structures of Electrodes and
Membranes..........................................................................................345
8.7 Fuel Cell Test Facility.........................................................................348
8.8 Summary.............................................................................................350
References...................................................................................................... 351
9. Fuel Cell Components and Design..........................................................353
9.1 Alkaline Fuel Cell..............................................................................353
9.1.1 AFC Basic Principles and Operations................................354
9.1.2 AFC Components and Configurations..............................355
9.1.3 AFC Electrolyte, Electrode, and Catalyst..........................358
9.1.3.1 Electrolyte............................................................... 359
9.1.3.2 Electrodes and Catalysts......................................360
9.1.3.3 Stack Configuration.............................................. 361
9.1.4 AFC Recent Advances.......................................................... 361
9.2 Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cell................................................................ 362
9.2.1 PAFC Basic Principles and Operations.............................. 362
9.2.2 PAFC Components and Configurations............................364
9.2.3 PAFC Electrolyte, Electrode, and Catalyst........................365
9.2.3.1 Electrolyte...............................................................366
9.2.3.2 Electrodes and Catalysts...................................... 367
9.2.3.3 Stack........................................................................ 367
9.2.4 PAFC Recent Advances........................................................368
9.3 Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell....................................... 369
9.3.1 PEMFC Operation and Design........................................... 369
9.3.1.1 Electrode Material and Structure....................... 370
9.3.1.2 Catalyst Layer........................................................ 371
9.3.1.3 Gas Diffusion Layer.............................................. 374
9.3.1.4 Electrolyte Membrane.......................................... 375
9.3.1.5 Nafion Membrane Construction......................... 376
9.3.1.6 Major Characteristics of Nafion-117
Membrane.............................................................. 377
9.3.1.7 Water Content in Nafion—PEM.......................... 378
9.3.1.8 Proton Conductivity in Nafion............................380
xvi Contents
9.3.1.9 Membrane Ionic Resistance and Ohmic
Loss................................................................... 382
9.3.1.10 Water Diffusivity in Nafion.................................383
9.3.1.11 Electro-Osmotic Drag Coefficient.......................384
9.4 Molten Carbonate Fuel Cell..............................................................386
9.4.1 MCFC Basic Principles and Operations............................386
9.4.2 MCFC Components and Configurations........................... 389
9.4.2.1 Fuels and Fuel Processing.................................... 389
9.4.2.2 Combustor.............................................................. 390
9.4.2.3 Cell and Stack Design........................................... 390
9.4.3 MCFC Electrolyte, Electrode, and Catalyst....................... 390
9.4.3.1 Electrolyte............................................................... 390
9.4.3.2 Cathode................................................................... 392
9.4.3.3 Anode...................................................................... 392
9.4.4 MCFC Recent Advances....................................................... 393
9.4.4.1 Material Development.......................................... 393
9.4.4.2 Fuel and Gas Turbine Hybrid Systems............... 393
9.5 Solid Oxide Fuel Cell......................................................................... 394
9.5.1 Basic Principles and Operation........................................... 395
9.5.1.1 SOFC Cell Designs................................................ 396
9.5.1.2 Planar Design......................................................... 397
9.5.2 Components of SOFC........................................................... 399
9.5.2.1 SOFC Electrolyte....................................................400
9.5.2.2 Zirconia Electrolyte............................................... 401
9.5.2.3 Scandia-Stabilized Zirconia (ScSZ).....................403
9.5.2.4 Ceria Electrolyte....................................................403
9.5.2.5 Gadolinia-Doped Ceria (GDC or GdCeO).........403
9.5.2.6 Samaria-Doped Ceria (SmCeO)..........................404
9.5.2.7 Yttria-Doped Ceria (YDC)...................................404
9.5.2.8 SOFC Anode Electrode.........................................404
9.5.2.9 SOFC Cathode Electrode......................................405
9.5.2.10 SOFC Interconnect................................................406
9.6 Direct Methanol Fuel Cell.................................................................406
9.6.1 Gas Diffusion Layer..............................................................408
9.6.2 Catalyst in DMFC.................................................................408
References......................................................................................................409
10. Fuel Cell Stack, Bipolar Plate, and Gas Flow Channel........................ 411
10.1 Fuel Cell Stack Design....................................................................... 411
10.2 Fuel Cell Stack and Power System................................................... 415
10.3 Water Removal and Management...................................................423
10.4 Cooling/Heating System for Fuel Cells.......................................... 424
10.5 Bipolar Plate Design..........................................................................428
10.5.1 Major Design Considerations..............................................428
10.5.2 Bipolar Plate Materials.........................................................430
Contents xvii
10.5.2.1 Metallic Bipolar Plates..........................................430
10.5.2.2 Graphite Bipolar Plate........................................... 432
10.5.2.3 Composite Bipolar Plate....................................... 432
10.5.3 Material Selection.................................................................433
10.6 Gas Flow-Field....................................................................................434
10.6.1 Gas Flow Channel Design...................................................435
10.6.2 Flow-Field Channel Layout Configurations..................... 437
10.6.2.1 Straight Parallel Channels................................... 437
10.6.2.2 Serpentine Flow Channel Design.......................440
10.6.2.3 Multiple Parallel Serpentine Channels with
Square Bends......................................................... 441
10.6.2.4 Pin-Array Flow-Field............................................ 441
10.6.2.5 Interdigitated Flow-Field......................................442
10.6.3 Simulation Analysis of Flow-Field.....................................442
10.6.3.1 Gas Channel...........................................................443
10.6.3.2 Flow in Parallel Straight Channels.....................445
10.6.3.3 Single Serpentine Channel..................................447
10.6.3.4 Single Serpentine Channel with Square
Bends.......................................................................448
10.6.3.5 Multiple Parallel Serpentine Channels with
Square Bends.........................................................450
Further Reading............................................................................................453
11. Simulation Model for Analysis and Design of Fuel Cells.................. 457
11.1 Zero-Order Fuel Cell Analysis Model............................................ 457
11.1.1 Activation Loss: ηact...............................................................458
11.1.2 Simplified Butler–Volmer Equation: Very Small ηact........ 459
11.1.3 Simplified Butler–Volmer Equation: Very Large ηact........ 459
11.1.4 Simplified Butler–Volmer Equation with Identical
Charge Transfer Coefficient................................................460
11.1.5 Ohmic Loss: ηohm................................................................... 461
11.1.6 Concentration Loss: ηconc...................................................... 462
11.2 One-Dimensional Fuel Cell Analysis Model.................................465
11.2.1 Anode Gas Channel.............................................................466
11.2.2 Anode Electrode................................................................... 467
11.2.3 Cathode Gas Channel..........................................................468
11.2.4 Cathode Electrode................................................................. 469
11.3 One-Dimensional Water Transport Model..................................... 469
11.3.1 Anode Gas Channel............................................................. 471
11.3.2 Anode Electrode...................................................................472
11.3.3 Cathode Gas Channel.......................................................... 473
11.3.4 Cathode Electrode................................................................. 473
11.3.5 Electrolyte Membrane.......................................................... 474
11.3.5.1 SOFC Electrolyte Membrane............................... 474
11.3.5.2 PEM Electrolyte Membrane................................. 475
xviii Contents
11.4 One-Dimensional Electrochemical Model..................................... 478
11.4.1 Activation Loss: ηact............................................................... 478
11.4.2 Ohmic Loss: ηohm...................................................................480
11.4.3 Ohmic Loss ηohm in Polymer Membrane...........................480
11.4.4 Water Content in Nafion–PEM............................................ 481
11.4.5 Mass Concentration Loss: ηconc............................................ 481
11.5 One-Dimensional Fuel Cell Thermal Analysis Model................. 494
11.5.1 A Simplified One-Dimensional Heat Transfer Model..... 497
11.6 Multi-Dimensional Model................................................................503
11.6.1 Two-Dimensional Model.....................................................504
11.6.2 Three-Dimensional Model..................................................505
11.6.2.1 Gas Channel...........................................................506
11.6.2.2 Flow in Porous Electrodes...................................508
11.6.2.3 Mass Transport......................................................508
11.6.2.4 Heat Transport Equation......................................509
11.6.2.5 Electrolyte Membrane.......................................... 510
11.6.2.6 Boundary Conditions........................................... 511
Further Reading............................................................................................ 514
12. Dynamic Simulation and Fuel Cell Control System............................ 517
12.1 Dynamic Simulation Model for Fuel Cell Systems....................... 517
12.1.1 System Dynamics.................................................................. 518
12.1.2 Block and Information Flow Diagram............................... 519
12.1.3 Solution Methodology for Dynamic Simulation.............. 522
12.2 Simulation of the Fuel Cell–Powered Vehicle................................ 524
12.2.1 Fuel Cell Vehicle Simulation............................................... 524
12.2.2 Simulation Model for PEMFC System............................... 527
12.2.3 Dynamic Simulation Model of the PEMFC Cell..............530
12.3 Dynamic Simulation of Integrated Fuel Cell Systems.................. 532
12.3.1 Regenerative PEM Fuel Cell System.................................. 532
12.3.2 Photovoltaic System..............................................................533
12.3.2.1 Solar Cell................................................................533
12.3.2.2 Simulink Model of PV System.............................536
12.3.2.3 Fuel Cell Subsystem.............................................. 537
12.3.2.4 Simulink Model and Results............................... 541
12.3.3 Molten Carbonate Fuel Cell System Model.......................545
12.3.3.1 Geometry................................................................547
12.3.3.2 Mass Balance..........................................................547
12.3.3.3 Reaction Rates........................................................549
12.3.3.4 Energy Balance...................................................... 551
12.3.3.5 Performance........................................................... 552
12.3.4 MATLAB/Simulink Simulation of MCFC.........................554
12.3.4.1 Steady-State Analysis............................................554
12.3.4.2 Transient Simulation.............................................555
12.4 Control System...................................................................................556
Contents xix
12.4.1 Fuel Cell System Control.....................................................556
12.4.2 Control Techniques...............................................................558
12.4.2.1 Control Problem Formulation.............................558
12.4.2.2 Control Configuration.......................................... 559
12.4.3 PID, Fuzzy Logic, and Neural Networks–Based
Control Systems.................................................................... 562
12.4.3.1 The PID Controller................................................ 562
12.4.3.2 Fuzzy Logic Control.............................................564
12.4.3.3 Input and Output Variables.................................565
12.4.3.4 Membership Functions.........................................565
12.4.3.5 Design of Fuzzy Control Rules...........................566
12.4.3.6 Inference................................................................. 567
12.4.3.7 Defuzzification......................................................568
12.4.3.8 Neural Networks................................................... 569
References...................................................................................................... 572
13. Fuel Cell Power Generation Systems...................................................... 575
13.1 Fuel Cell Subsystems......................................................................... 575
13.1.1 Fuel Processing...................................................................... 575
13.1.2 Fuel Cell Auxiliary............................................................... 577
13.1.3 Power Electronics and Power Conditioning..................... 577
13.1.4 Thermal and Water Management.......................................580
13.1.5 System Efficiency..................................................................580
13.1.6 System Integration................................................................ 582
13.2 Fuels and Fuel Processing.................................................................583
13.2.1 Basic Fuels and Processes....................................................583
13.2.2 Desulfurization.....................................................................586
13.2.3 Steam Reforming.................................................................. 587
13.2.4 Partial Oxidation Reforming............................................... 589
13.2.5 Autothermal Reforming...................................................... 591
13.2.6 Water Shift Reaction............................................................. 591
13.2.7 Coal Gasification................................................................... 592
13.2.8 Carbon Monoxide Removal................................................. 593
13.3 Hydrogen as Energy Carrier............................................................ 594
13.3.1 Hydrogen Generation Methods.......................................... 595
13.3.1.1 Fossil Fuels and Biomass...................................... 595
13.3.1.2 Electrolysis............................................................. 596
13.3.1.3 Thermochemical Water Splitting........................ 598
13.3.1.4 Photocatalysis........................................................ 599
13.3.1.5 Biohydrogen........................................................... 601
13.3.1.6 By-Product of Chemical Production
Processes..............................................................603
13.3.2 Hydrogen Storage.................................................................603
13.3.2.1 Physical Storage.....................................................605
13.3.2.2 Chemical Storage...................................................607
xx Contents
13.3.3 Transportation and Distribution........................................608
13.3.4 Hydrogen Safety...................................................................609
13.4 Summary............................................................................................. 610
References...................................................................................................... 611
14. Fuel Cell Application, Codes and Standards, and
Environmental Effects................................................................................ 613
14.1 Fuel Cell Applications....................................................................... 614
14.1.1 Stationary Power................................................................... 614
14.1.2 Transportation Power........................................................... 615
14.1.3 Portable Applications........................................................... 616
14.1.4 Military Applications........................................................... 616
14.1.5 Landfills and Other Applications....................................... 617
14.2 Fuel Cell Codes and Standards........................................................ 618
14.2.1 Stationary and Portable Fuel Cell Commercial Systems.... 619
14.2.2 Hydrogen Vehicle and Infrastructure Codes and
Standards............................................................................... 621
14.2.3 Scope of Key Codes and Standards.................................... 625
14.3 Environmental Effects....................................................................... 632
14.3.1 Fuel Cell Emissions.............................................................. 632
14.3.2 Fuel Cell Life Cycle Assessment.........................................635
14.4 Summary.............................................................................................640
References...................................................................................................... 641
Nomenclature......................................................................................................643
Appendix A: Constants and Conversion Units............................................ 657
Appendix B: Useful Equations for Fuel Cell Calculations........................659
Appendix C: Chemical and Thermodynamic Data..................................... 671
专业书籍
下载地址:(回复后可见)
| ![]()