马上注册,结交更多好友,享用更多功能,让你轻松玩转社区。
您需要 登录 才可以下载或查看,没有账号?立即注册
×
《Principles of Turbomachinery in Air-Breathing Engines》
气动发动机叶轮机械的工作原理
作者:ERIAN A. BASKHARONE
Texas A&M University
出版社:Cambridge
出版时间:2006年
《Principles of Turbomachinery in Air-Breathing Engines》

《Principles of Turbomachinery in Air-Breathing Engines》

《Principles of Turbomachinery in Air-Breathing Engines》

《Principles of Turbomachinery in Air-Breathing Engines》
目录
1 Introduction to Gas-Turbine Engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Definition 1
Advantages of Gas-Turbine Engines 1
Applications of Gas-Turbine Engines 3
The Gas Generator 3
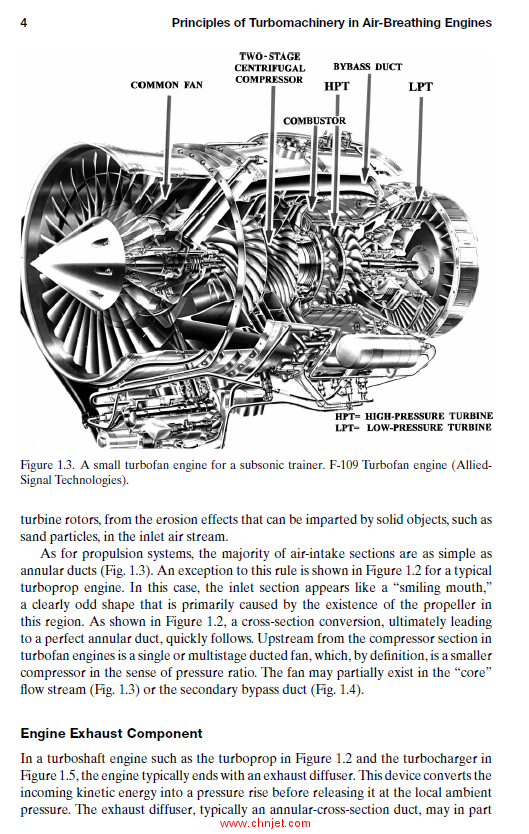
Air Intake and Inlet Flow Passage 3
Engine-Exhaust Component 4
Multispool Engine Arrangements 6
Thermodynamic Cycle in a Single-Combustor Engine 6
Importance of Metallurgical Progress 7
2 Overview of Turbomachinery Nomenclature . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Definition of a Turbomachine 9
General Classification of Turbomachines 10
Stage Definition 15
Coordinate System 16
Velocity Diagrams 17
Multiple Staging 20
Viscosity and Compressibility Factors 22
Stator/Rotor Interaction 25
3 Aerothermodynamics of Turbomachines
and Design-Related Topics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
Assumptions and Limitations 26
Energy-Conservation Law 29
Introduction of Total Properties 29
Ideal Gas as a Working Medium 29
Entropy-Based Loss Coefficient 36
ix
x Contents
Compressibility of the Working Medium 39
Sonic Speed in Ideal Gases 39
Mach Number and Compressibility of a Flow Field 40
Total Properties in Terms of the Mach Number 40
Definition of the Critical Mach Number 41
Total Properties in Terms of the Critical Mach Number 43
Definition of the Pitch Line in Turbomachines 45
Continuity Equation in Terms of Total Properties 46
Isentropic Flow in Varying-Area Passages 48
The Sonic State 51
Nozzle- and Diffuser-Like Airfoil Cascades 52
Bernoulli’s Equation: Applicability and Limitations 54
Favorable and Unfavorable Pressure Gradients 58
Design-Point and Off-Design Operating Modes 63
Choice of the Design Point 64
Variable-Geometry Turbomachines 65
Means of Assessing Turbomachinery Performance 70
Total Relative Flow Properties 74
Introduction of the Relative Critical Mach Number 75
Losses in Constant-Area Annular Ducts (Fanno Line) 77
Fanno-Flow Relationships 80
Exhaust Diffusers 94
Definition of the Momentum Thickness 97
Problems 103
4 Energy Transfer between a Fluid and a Rotor . . . . . . . . . 112
Stationary and Rotating Frames of Reference 115
Flow and Airfoil Angles 119
Components of Energy Transfer 120
Definition of the Stage Reaction 122
Reaction of Axial-Flow Stages 122
Invariant Thermophysical Properties 124
The Total Enthalpy (ht ) 124
The Total Relative Enthalpy (ht r ) 124
The Rothalpy (I) 125
Importance of the Invariant Properties 125
Total Relative Properties 128
Incidence and Deviation Angles 131
Problems 157
5 Dimensional Analysis, Maps, and Specific Speed . . . . . .172
Introduction 172
Geometrical Similarity 172
Dynamic Similarity 172
Contents xi
Buckingham’s π Theorem: Incompressible Flows 173
Application of Buckingham’s Theorem to Compressible-Flow
Turbomachines 173
Compressor and Turbine Maps 175
Choking of Compressors and Turbines 178
Specific Speed 180
Application of Specific Speed to Incompressible-Flow
Turbomachines 182
Application of Specific Speed to Compressible-Flow
Turbomachines 183
Design Role of Specific Speed 185
Traditional Specific Speed Approximations 186
Problems 200
6 Radial-Equilibrium Theory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 208
Assumptions 208
Implications 208
Derivation of the Radial-Equilibrium Equation 210
Special Forms of the Radial-Equilibrium Equation 213
Further Simplifications 214
Problems 226
7 Polytropic (Small-Stage) Efficiency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .234
Derivation of the Polytropic Efficiency 234
Multistage Compressors and Turbines 237
Problems 243
8 Axial-Flow Turbines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .250
Stage Definition 250
The Preliminary Design Process 250
Stage Design: A Simplified Approach 255
Definitions of the Incidence and Deviation Angles 276
Detailed Design of Airfoil Cascades 280
Airfoil-Cascade Geometry Variables 283
Airfoil Aerodynamic Loading 285
Geometrical Discontinuities 287
Performance-Controlling Variables 290
Aspect Ratio 290
Tip-Clearance Effects 291
Reynolds Number Effect 294
Incidence-Angle Effect 295
Suction-Side Flow Diffusion 296
Location of the Front Stagnation Point 299
Trailing-Edge Thickness 300
xii Contents
Design-Oriented Empirical Correlations 301
Stacking of the Vane and Blade Airfoil Sections 304
Shaft-Work Extraction in Low-Aspect-Ratio Blades 306
The Supersonic Stator Option 306
Shape of the Stagnation Streamlines 312
Simple Component Adaptation Means 313
Hot-to-Cold Dimensions’ Conversion 314
Cooling Flow Extraction and Path of Delivery 316
Problems 335
9 Axial-Flow Compressors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .347
Introduction 347
Comparison with Axial-Flow Turbines 347
Stage Definition and Multiple Staging 350
Normal Stage Definition 352
Standard Airfoil Profiles 354
Real Flow Effects 357
Compressor Off-Design Characteristics 360
Rotating Stall and Total Surge 360
Compressor Behavior during Start-up 363
Means of Suppressing Start-up Problems 364
Problems 385
10 Radial-Inflow Turbines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 398
Introduction 398
Components of Energy Transfer 398
Flow Angles 399
Stage Reaction 400
Other Performance-Related Dimensionless Variables 401
Total Relative Properties and Critical Mach Number 402
Conventional-Stage Geometrical Configurations 403
Compressibility Effects 408
Stage-Design Approach 415
Closed-Form Loss Correlations 418
Effect of the “Scallop” Radius and Backface Clearance 425
Stage Placement in a Multistage Turbine 454
Cooling Techniques 455
Problems 458
11 Centrifugal Compressors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 471
Component Identification 472
Impeller Inlet System 475
Inlet-Duct Total Pressure Loss 475
Compressor Thermodynamics 476
Contents xiii
Impeller Blading Options 477
Components of Energy Transfer and Stage Reaction 481
Performance Consequences of the Static Head 482
Performance Consequences of the Dynamic Head 485
Acceleration Components within the Impeller 486
Slip Phenomenon 488
Slip Factor 488
Stage Total-to-Total Efficiency 489
Volute Flow Field 489
One-Dimensional Approach to Volute Design 492
Total-to-Static Efficiency 493
Tip-Clearance Effect 494
Multiple Staging 495
Impeller/Stator Unsteady Flow Interaction 496
Problems 515
12 Turbine-Compressor Matching . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 529
Problem Category 1 533
Problem Category 2 536
Performance-Related Variables in Propulsion Systems 538
Gas Generator Operating Lines on Compressor Maps:
Constant Tt4/Tt2 Lines 541
Required Post-processing Work 544
Problems 560
References 573
Index 575
专业书籍
下载地址:(回复后可见)
| ![]()