马上注册,结交更多好友,享用更多功能,让你轻松玩转社区。
您需要 登录 才可以下载或查看,没有账号?立即注册
×
《Ageing of composites》
复合材料老化
编辑:Rod Martin
出版社:WP
出版时间:2008年
《Ageing of composites》

《Ageing of composites》

《Ageing of composites》

《Ageing of composites》
目录
Contributor contact details xii
Introduction xix
Part I Ageing of composites – processes and
modelling 1
1 The physical and chemical ageing of polymeric
composites 3
T. Gates, formerly NASA Langley Research Center, USA
1.1 Introduction 3
1.2 Background 7
1.3 Viscoelasticity 10
1.4 Ageing and effective time 15
1.5 Development of an ageing study 22
1.6 Summary 28
1.7 References 29
2 Ageing of glass–ceramic matrix composites 34
K. Plucknett, Dalhousie University, Canada
2.1 Introduction 34
2.2 Composite fabrication 42
2.3 Fast-fracture behaviour 42
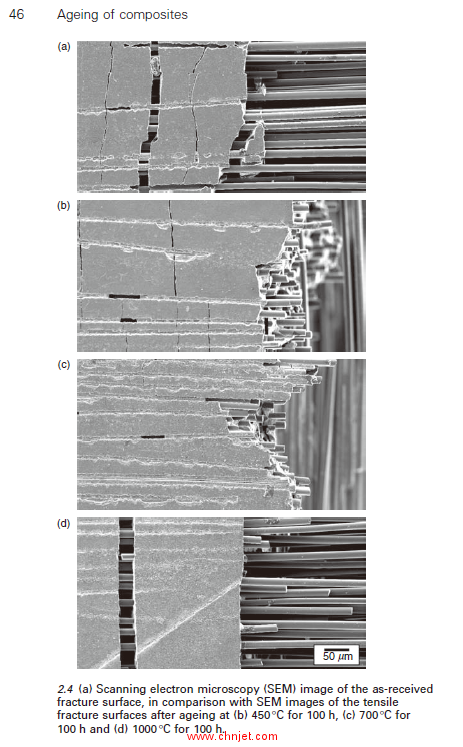
2.4 Long-term environmental ageing behaviour 43
2.5 Mechanism of oxidation degradation 51
2.6 Development of a failure mechanism map 57
2.7 Oxidation behaviour under applied stress 57
2.8 Thermal shock cycling 62
v
© 2008, Woodhead Publishing Limited except Chapter 6
vi Contents
2.9 Composite protection methods 62
2.10 Conclusions and future trends 63
2.11 References 64
3
reinforced concrete 71
H. Cuypers, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Belgium;
and J. Orlowsky, Institut für Bauforschung der
RWTH Aachen, Germany
3.1 Introduction 71
72
3.3 Experimental methods 74
3.4 76
3.5 Interface effects 90
3.6 Composite loading effects 91
3.7 In situ degradation of composites due to chemical attack 92
3.8 Conclusions 96
3.9 Acknowledgements 97
3.10 References 97
4 Stress corrosion cracking in glass reinforced
polymer composites 100
A. Chateauminois, Ecole Supérieure de Physique et
Chimie Industrielles (ESPCI), France
4.1 Introduction 100
4.2 Overview of stress corrosion cracking in glass reinforced
polymer matrix composites 101
4.3 107
4.4
reinforced polymer composites 115
4.5 Concluding remarks and future trends 124
4.6 References 126
5 Thermo-oxidative ageing of composite materials 130
T. Tsotsis, The Boeing Company, USA
5.1 Introduction 130
5.2 Developments in understanding thermo-oxidative
ageing 136
5.3 Initial studies – Kerr and Haskins 136
5.4 Overview of other studies 138
5.5 Areas for future study 150
5.6 Conclusions and recommendations 153
5.7 References 154
Chemical ageing mechanisms of glass fibre
3.2 Problem identification
Modelling of the chemical attack of fibres
Stress corrosion cracking of glass fibres
Stress corrosion cracking in unidirectional glass fibre
© 2008, Woodhead Publishing Limited except Chapter 6
Contents vii
6 Fourier transform infrared photoacoustic
spectroscopy of ageing composites 160
R. W. Jones and J. McClelland, Iowa State University,
USA
6.1 Introduction 160
6.2 Theory and practice of photoacoustic spectroscopy 161
6.3 Ageing of composites 170
6.4 Ambient temperature ageing of prepreg 180
6.5 Acknowledgements 180
6.6 References 182
7 Modeling physical ageing in polymer composites 186
H. Hu, National Pingtung University of Science and
Technology, Taiwan
7.1 Introduction 186
7.2 Modeling physical ageing in short-term creep 187
7.3 Modeling physical ageing in long-term creep 200
7.4 Temperature and moisture effects 203
7.5 Conclusions 204
7.6 References 204
8 Ageing of silicon carbide composites 206
S. M. Skolianos, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki,
Greece
8.1 Introduction 206
8.2 Silicon carbide composites 206
8.3 Ageing kinetics 208
8.4 Microstructural change 211
8.5 Effect of volume fraction and size of silicon carbide
reinforcement 214
8.6 Changes in properties 217
8.7 References 220
9 Modelling accelerated ageing in polymer
composites 224
G. Mensitieri, CR-INSTM – University of Naples
Federico II, Italy; and M. Iannone, Alenia Aeronautica
s.p.a., Italy
9.1 Introduction 224
variables 226
9.3 Degradation mechanisms and processes 227
9.4 Modelling time-dependent mechanical behaviour 233
9.2 Definition of environmental conditions and important
© 2008, Woodhead Publishing Limited except Chapter 6
viii Contents
9.5 Modelling mechanical degradation 240
9.6 Modelling physical ageing 241
9.7 Modelling hygrothermal effects 246
9.8 Modelling chemical ageing 254
9.9 Methodology for accelerated testing based on the
modelling approach 256
9.10 Accelerated long-time mechanical behaviour 257
9.11 Accelerated mechanical degradation 270
9.12 Accelerated physical ageing 272
9.13 Accelerated hygrothermal degradation 272
9.14 Accelerated thermal degradation and oxidation 273
9.15 Validation of acceleration procedure by comparison
with real-time data 275
9.16 Future trends 276
9.17 References 276
Part II Ageing of composites in transport applications 283
10 Ageing of composites in the rail industry 285
K. B. Shin, HANBAT National University, Korea
10.1 Introduction 285
10.2 The major environmental ageing factors and their effects
on composites for rail vehicle applications 290
10.3 Environmental test methods and evaluation procedures
for ageing of composites 291
10.4 Case study: evaluation of the effect of increased
composite ageing on the structural integrity of the
bodyshell of the Korean tilting train 302
10.5 Conclusions 308
10.6 References 309
11 Ageing of composites in the rotorcraft industry 311
K. Dragan, Polish Air Force Institute of
Technology, Poland
11.1 Introduction to composite structures applied in the
rotorcraft industry using the example of PZL 311
11.2 Potential damage that can occur in a composite main
rotor blade 313
11.3 Low-energy impact damage and durability in a W-3 main
rotor blade 317
321
11.5 New techniques for testing composite structures 323
11.6 References 324
11.4 Influence of moisture and temperature
© 2008, Woodhead Publishing Limited except Chapter 6
Contents ix
12 Ageing of composites in marine vessels 326
P. Davies and D. Choqueuse, IFREMER Brest
Centre, France
12.1 The use of composites in marine vessels 326
12.2 Marine composites 328
12.3 The marine environment 330
12.4 Recent published studies on marine ageing 331
12.5 Example 1: glass-reinforced thermoset ageing 337
12.6 Example 2: ageing at sea 339
12.7 Example 3: osmosis and blistering 342
12.8 Relevance of accelerated tests 344
12.9 Conclusions and future trends 349
12.10 References 349
Part III Ageing of composites in non-transport
applications 355
13 Ageing of polyethylene composite implants in
medical devices 357
S. Affatato, Istituti Ortopedici Rizzoli, Italy
357
13.2 Brief history of polyethylene used in
medical devices 360
13.3 Improvements on polyethylene for
medical devices 364
13.4 Ageing of polyethylene 367
13.5 Future trends 369
13.6 Acknowledgements 370
13.7 References 370
14 Ageing of composites in oil and gas applications 375
S. Frost, ESR Technology Ltd, UK
14.1 Introduction 375
14.2 Modelling of damage 377
14.3 Ageing due to temperature 384
14.4 Ageing due to chemical species 386
14.5 Ageing due to applied load 389
14.6 Design against ageing 393
14.7 Assessment of ageing 394
14.8 Examples of ageing 397
14.9 Conclusions 398
14.10 References 399
13.1 Definition of medical devices
© 2008, Woodhead Publishing Limited except Chapter 6
x Contents
15 Ageing of composites in the construction industry 401
S. Halliwell, NetComposites Ltd, UK
15.1 Introduction 401
402
405
15.4 Performance requirements 406
15.5 Performance in service 407
15.6 Joints 417
15.7
structures 418
15.8 Summary 418
15.9 Sources of further information and advice 419
15.10 References 419
16 Ageing of composite insulators 421
S. M. Gubanski, Chalmers University of Technology,
Sweden
16.1 High-voltage insulators 421
16.2 Materials and manufacturing techniques 423
16.3 Practical experiences with composite insulators 424
16.4 Ageing of insulator housing 428
16.5 Ageing of insulator cores 439
16.6 Ageing at insulator interfaces 440
16.7 Future trends 442
16.8 Acknowledgements 443
16.9 References 443
17 Ageing of composites in the chemical processing
industry 448
R. Martin, Materials Engineering Research
Laboratory Ltd, UK
17.1 Introduction 448
17.2
chemical processing industry 451
17.3 452
17.4 452
17.5 Current methods for assessing long-term ageing
454
17.6 Case studies of ageing assessment approaches 457
17.7 Concluding remarks 464
17.8 References 465
15.2 Use of fibre-reinforced polymers in construction
15.3 Benefits of fibre-reinforced polymers for construction
Repair of degraded fibre-reinforced polymer composite
Examples of use of fibre reinforced plastics in the
Types of fibre reinforced plastic
Types of degradation in fibre reinforced plastic
of fibre reinforced plastics
© 2008, Woodhead Publishing Limited except Chapter 6
Contents xi
18 Ageing of composites in underwater applications 467
D. Choqueuse and P. Davies, IFREMER Brest Centre,
France
18.1 Introduction 467
18.2 Deep sea environmental parameters 468
18.3 Ageing of composites in water 472
18.4 Case study 1: composite tubes 478
18.5 Case study 2: composite material for deep sea
applications 483
18.6 Case study 3: syntactic foam for deep sea and offshore
applications 489
18.7 Concluding remarks 496
18.8 References 496
专业书籍
下载地址:(回复后可见)
|
![]()