马上注册,结交更多好友,享用更多功能,让你轻松玩转社区。
您需要 登录 才可以下载或查看,没有账号?立即注册
×
《Fuel Processing for Fuel Cells》
燃料电池的燃料处理
作者:Dr. Gunther Kolb
IMM - Institut für Mikrotechnik Mainz GmbH
出版社:Wiley
出版时间:2008年
《Fuel Processing for Fuel Cells》

《Fuel Processing for Fuel Cells》

《Fuel Processing for Fuel Cells》

《Fuel Processing for Fuel Cells》
目录
Acknowledgement IX
1 Introduction and Outline 1
2 Fundamentals 3
2.1 Common Fossil Fuels 3
2.2 Basic Definitions, Calculations and Legislation 6
2.3 The Various Types of Fuel Cells and the Requirements of the
Fuel Processor 12
2.3.1 PEM Fuel Cells 12
2.3.2 High Temperature Fuel Cells 15
3 The Chemistry of Fuel Processing 17
3.1 Steam Reforming 17
3.2 Partial Oxidation 22
3.3 Oxidative Steam Reforming or Autothermal Reforming 29
3.4 Catalytic Cracking of Hydrocarbons 38
3.5 Pre-Reforming of Higher Hydrocarbons 39
3.6 Homogeneous Plasma Reforming of Higher Hydrocarbons 43
3.7 Aqueous Reforming of Bio-Fuels 44
3.8 Processing of Alternative Fuels 44
3.8.1 Dimethyl Ether 44
3.8.2 Methylcyclohexane 45
3.8.3 Sodium Borohydride 45
3.8.4 Ammonia 46
3.9 Desulfurisation 46
3.10 Carbon Monoxide Clean-Up 48
3.10.1 Water–Gas Shift 48
3.10.2 Preferential Oxidation of Carbon Monoxide 49
3.10.3 Methanation 51
V
3.11 Catalytic Combustion 52
3.12 Coke Formation on Metal Surfaces 52
4 Catalyst Technology for Distributed Fuel Processing Applications 57
4.1 A Brief Introduction to Catalyst Technology and Evaluation 57
4.1.1 Catalyst Activity 58
4.1.2 Catalyst Stability 60
4.1.3 Catalyst Coating Techniques 61
4.1.4 Specific Features Required for Fuel Processing Catalysts
in Smaller Scale Applications 68
4.2 Reforming Catalysts 69
4.2.1 Catalysts for Methanol Reforming 71
4.2.2 Catalysts for Ethanol Reforming 77
4.2.3 Overview of Catalysts for Hydrocarbon Reforming 80
4.2.4 Catalysts for Natural Gas/Methane Reforming 81
4.2.5 Catalysts for Reforming of LPG 84
4.2.6 Catalysts for Pre-Reforming of Hydrocarbons 86
4.2.7 Catalysts for Gasoline Reforming 88
4.2.8 Catalysts for Diesel and Kerosene Reforming 92
4.2.9 Cracking Catalysts 96
4.2.10 Deactivation of Reforming Catalysts by Sintering 98
4.2.11 Deactivation of Reforming Catalysts by Coke Formation 98
4.2.12 Deactivation of Reforming Catalysts by Sulfur Poisoning 101
4.3 Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Alternative Fuels 105
4.3.1 Dimethyl Ether 105
4.3.2 Methylcyclohexane 106
4.3.3 Sodium Borohydride 107
4.3.4 Ammonia 107
4.4 Desulfurisation Catalysts/Adsorbents 108
4.5 Carbon Monoxide Clean-Up Catalysts 111
4.5.1 Catalysts for Water–Gas Shift 111
4.5.2 Catalysts for the Preferential Oxidation of Carbon Monoxide 116
4.5.3 Methanation Catalysts 123
4.6 Combustion Catalysts 124
5 Fuel Processor Design Concepts 129
5.1 Design of the Reforming Process 129
5.1.1 Steam Reforming 129
5.1.2 Partial Oxidation 146
5.1.3 Autothermal Reforming 149
5.1.4 Catalytic Cracking 154
5.1.5 Pre-Reforming 155
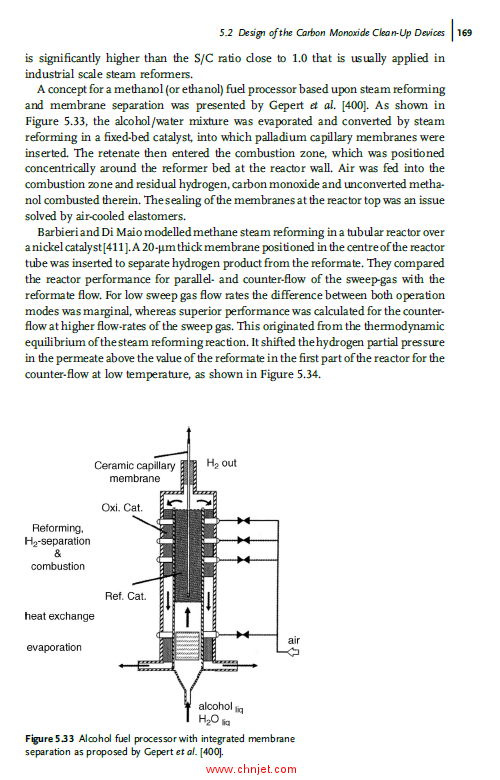
5.2 Design of the Carbon Monoxide Clean-Up Devices 155
5.2.1 Water–Gas Shift 155
5.2.2 Preferential Oxidation of Carbon Monoxide 161
VI Contents
5.2.3 Selective Methanation of Carbon Monoxide 164
5.2.4 Membrane Separation 164
5.2.5 Pressure Swing Adsorption 174
5.3 Aspects of Catalytic Combustion 176
5.4 Design of the Overall Fuel Processor 181
5.4.1 Overall Heat Balance of the Fuel Processor 181
5.4.2 Interplay of the Different Fuel Processor or Components 188
5.4.3 Overall Water Balance of the Fuel Processor 190
5.4.4 Overall Basic Engineering of the Fuel Processor 192
5.4.5 Dynamic Simulation of the Fuel Processor 205
5.4.6 Control Strategies for Fuel Processors 213
5.5 Comparison with Conventional Energy Supply Systems 215
6 Types of Fuel Processing Reactors 217
6.1 Fixed-Bed Reactors 217
6.2 Monolithic Reactors 217
6.3 Plate Heat-Exchanger Reactors 221
6.3.1 Conventional Plate Heat-Exchanger Reactors 223
6.3.2 Microstructured Plate Heat-Exchanger Reactors 225
7 Application of Fuel Processing Reactors 227
7.1 Reforming Reactors 227
7.1.1 Reforming in Fixed-Bed Reactors 227
7.1.2 Reforming in Monolithic Reactors 230
7.1.3 Reforming in Plate Heat-Exchanger Reactors 240
7.1.4 Reforming in Membrane Reactors 254
7.1.5 Reforming in Chip-Like Microreactors 260
7.1.6 Plasmatron Reformers 264
7.2 Water–Gas Shift Reactors 269
7.2.1 Water–Gas Shift in Monolithic Reactors 269
7.2.2 Water–Gas Shift in Plate Heat-Exchanger Reactors 270
7.2.3 Water–Gas Shift in Membrane Reactors 272
7.3 Catalytic Carbon Monoxide Fine Clean-Up 272
7.3.1 Carbon Monoxide Fine Clean-Up in Fixed-Bed Reactors 272
7.3.2 Carbon Monoxide Fine Clean-Up in Monolithic Reactors 273
7.3.3 Carbon Monoxide Fine Clean-Up in Plate Heat-Exchanger
Reactors 275
7.3.4 Carbon Monoxide Fine Clean-Up in Membrane Reactors 282
7.4 Membrane Separation Devices 283
7.5 Catalytic Burners 285
8 Balance-of-Plant Components 289
8.1 Heat-Exchangers 289
8.2 Liquid Pumps 290
8.3 Blowers and Compressors 290
Contents VII
8.4 Feed Injection System 292
8.5 Insulation Materials 293
9 Complete Fuel Processor Systems 295
9.1 Methanol Fuel Processors 295
9.2 Ethanol Fuel Processors 316
9.3 Natural Gas Fuel Processors 317
9.4 Fuel Processors for LPG 327
9.5 Gasoline Fuel Processors 332
9.6 Diesel and Kerosine Fuel Processors 344
9.7 Multi-Fuel Processors 348
9.8 Fuel Processors Based on Alternative Fuels 350
10 Introduction of Fuel Processors Into the Market Place – Cost
and Production Issues 355
10.1 Factors Affecting the Cost of Fuel Processors 355
10.2 Production Techniques for Fuel Processors 359
10.2.1 Fabrication of Ceramic and Metallic Monoliths 359
10.2.2 Fabrication of Plate Heat-Exchangers/Reactors 361
10.2.3 Fabrication of Microchannels 365
10.2.4 Fabrication of Chip-Like Microreactors 367
10.2.5 Fabrication of Membranes for Hydrogen Separation 369
10.2.6 Automated Catalyst Coating 370
References 373
Index 409
专业书籍
下载地址:(回复后可见)
| ![]()