马上注册,结交更多好友,享用更多功能,让你轻松玩转社区。
您需要 登录 才可以下载或查看,没有账号?立即注册
×
《Flight Mechanics Modeling and Analysis》
飞行力学建模与分析
作者:
Jitendra R. Raol
Jatinder Singh
出版社:CRC
出版时间:2009年
《Flight Mechanics Modeling and Analysis》

《Flight Mechanics Modeling and Analysis》

《Flight Mechanics Modeling and Analysis》

《Flight Mechanics Modeling and Analysis》

《Flight Mechanics Modeling and Analysis》
目录
Preface..................................................................................................................... xv
Acknowledgments................................................................................................. xvii
Authors................................................................................................................... xix
Chapter 1 Introduction.......................................................................................... 1
1.1 ANNs in Control............................................................................................ 4
1.2 FL=S in Control ............................................................................................. 5
1.3 Evaluation of Aircraft Control–Pilot Interactions.......................................... 6
1.4 Chapter Highlights ......................................................................................... 7
References ................................................................................................................. 9
Chapter 2 Mathematical Model Building........................................................... 11
2.1 Introduction .................................................................................................. 11
2.2 Mathematical Model Structures ................................................................... 15
2.2.1 TF Models......................................................................................... 16
2.2.1.1 Continuous-Time Model ..................................................... 17
2.2.1.2 Discrete-Time Model .......................................................... 22
2.2.1.3 Delta Form TF..................................................................... 23
2.2.2 State-Space Models........................................................................... 26
2.2.2.1 State-Space Representations................................................ 28
2.2.2.2 General Model..................................................................... 33
2.2.3 Time-Series Models .......................................................................... 34
2.3 Models for Noise=Error Processes ............................................................... 37
2.3.1 Continuous-Time=Discrete-Time White=Correlated
Noise Processes................................................................................. 37
2.4 ANN Modeling ............................................................................................ 38
2.4.1 Feed Forward Neural Networks........................................................ 42
2.4.2 A Training Algorithm for FFNN...................................................... 42
2.4.3 Recurrent Neural Networks .............................................................. 44
2.5 FL-Based Modeling ..................................................................................... 45
2.5.1 Additive Fuzzy System..................................................................... 46
Epilogue .................................................................................................................. 50
Exercises ................................................................................................................. 50
References ............................................................................................................... 51
Chapter 3 Equations of Motion.......................................................................... 53
3.1 Introduction .................................................................................................. 53
3.2 Rigid Body EOM......................................................................................... 54
vii
3.3 Resolution of Inertial Forces and Moments ................................................ 60
3.4 Resolution of Aerodynamics, Gravity Forces, and Thrust Forces .............. 62
3.5 Complete Sets of EOM................................................................................ 67
3.5.1 Rectangular Form.............................................................................. 68
3.5.2 Polar Form ........................................................................................ 69
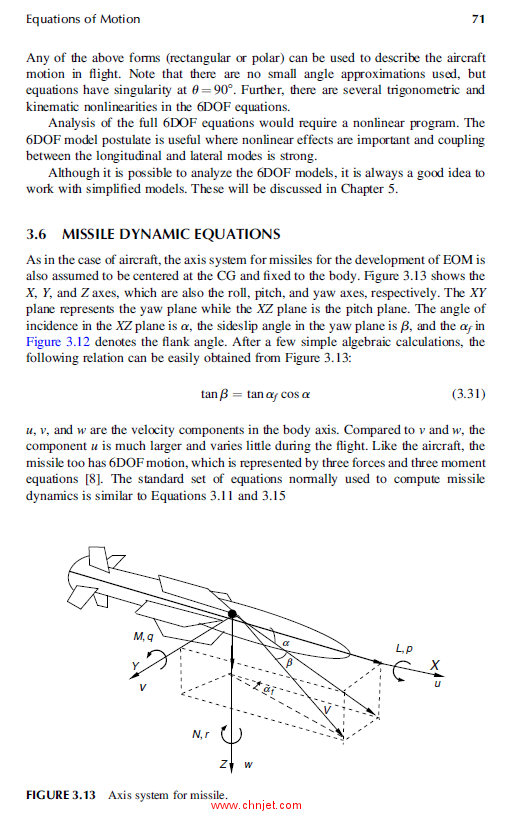
3.6 Missile Dynamic Equations ......................................................................... 71
3.7 Rotorcraft Dynamics .................................................................................... 72
3.7.1 Momentum Theory ........................................................................... 74
3.7.2 Blade-Element Theory ...................................................................... 76
3.7.3 Rotorcraft Modeling Formulations ................................................... 76
3.7.4 Limitations of Rigid Body Model .................................................... 78
Epilogue .................................................................................................................. 79
Exercises ................................................................................................................. 79
References ............................................................................................................... 80
Chapter 4 Aerodynamic Derivatives and Modeling........................................... 83
4.1 Introduction .................................................................................................. 83
4.2 Basic Aerodynamic Forces and Moments ................................................... 84
4.3 Aerodynamic Parameters ............................................................................. 86
4.3.1 Definition of Aerodynamic Derivatives............................................ 87
4.3.2 Longitudinal Derivatives................................................................... 90
4.3.3 Lateral-Directional Derivatives....................................................... 100
4.3.4 Compound Lateral-Directional Derivatives .................................... 106
4.4 Missile Aerodynamic Derivatives.............................................................. 107
4.4.1 Longitudinal Derivatives................................................................. 109
4.4.2 Lateral-Directional Derivatives....................................................... 109
4.4.2.1 Roll Derivatives ................................................................ 109
4.4.2.2 Yaw Derivatives................................................................ 110
4.5 Rotorcraft Aerodynamic Derivatives ......................................................... 111
4.6 Role of Derivatives in Aircraft Design Cycle and Flight Control
Law Development...................................................................................... 113
4.7 Aircraft Aerodynamic Models ................................................................... 116
Epilogue ................................................................................................................ 118
Exercises ............................................................................................................... 118
References ............................................................................................................. 119
Chapter 5 Simplification of Equations of Motion and Transfer-Function
Analysis ........................................................................................... 121
5.1 Introduction ................................................................................................ 121
5.2 Strategies for Simplification....................................................................... 122
5.2.1 Choice of Coordinate Systems ....................................................... 122
5.2.2 Linearization of Model Equations .................................................. 123
5.2.3 Simplification Using Measured Data.............................................. 124
viii
5.3 Longitudinal Models and Modes............................................................... 125
5.3.1 Short Period Mode........................................................................ 128
5.3.2 Phugoid ......................................................................................... 133
5.4 Lateral-Directional Models and Modes ..................................................... 136
5.4.1 DR Mode ...................................................................................... 137
5.4.2 Spiral Mode................................................................................... 139
5.4.3 Roll Mode ..................................................................................... 140
5.5 Missile Aerodynamic Transfer Functions.................................................. 142
5.6 Rotorcraft Linear Modeling ....................................................................... 145
5.6.1 Rotor Plus Body Models .............................................................. 146
5.6.2 Stability Derivative Models .......................................................... 147
5.6.3 Rotor-Response Decomposition Models ...................................... 148
5.6.4 Evaluation=Validation of Linear Flight Dynamics Models.......... 149
5.7 UAV Dynamics.......................................................................................... 150
5.8 MAV Dynamics......................................................................................... 151
5.9 Lighter-than-Air Vehicle=BLIMP Dynamics............................................. 153
Epilogue ................................................................................................................ 154
Exercises ............................................................................................................... 155
References ............................................................................................................. 156
Chapter 6 Simulation of Flight Dynamics ....................................................... 159
6.1 Introduction ................................................................................................ 159
6.2 Aircraft Subsystems Data=Models ............................................................. 163
6.2.1 Aero Database............................................................................... 164
6.2.2 Mass, Inertia, and Center of Gravity Characteristics.................... 164
6.2.3 Instrumentation System................................................................. 165
6.2.4 Inertial Navigation System ........................................................... 165
6.2.5 Flight Management System .......................................................... 165
6.2.6 Actuator Models............................................................................ 166
6.2.7 Engine Model................................................................................ 167
6.2.8 Landing Gear ................................................................................ 168
6.2.9 Control Loading and Sound Simulation ....................................... 168
6.2.10 Motion Cues.................................................................................. 169
6.2.11 Turbulence and Gust Models........................................................ 170
6.2.12 Sensor Modeling ........................................................................... 170
6.2.13 Flight Dynamics............................................................................ 171
6.3 Steady-State Flight and Trim Conditions .................................................. 171
6.3.1 Rate of Climb and Turn Coordination Flights ............................. 174
6.3.2 Computation of Linear Models for Control Law Design............. 176
6.4 Six DOF Simulation and Validation.......................................................... 178
6.4.1 Flight Simulation Model Validation for a Rotorcraft................... 180
6.4.2 Flight Simulation Model Validation Using the Concept
of Coefficient Matching ................................................................ 181
6.4.3 Flight Simulation Model Validation Using Direct Update........... 183
ix
6.5 PC MATLAB1=SIMULINK1-Based Simulation .................................... 184
Epilogue ................................................................................................................ 188
Exercises ............................................................................................................... 189
References ............................................................................................................. 190
Chapter 7 Flight Test Maneuvers and Database Management ........................ 193
7.1 Introduction ................................................................................................ 193
7.2 Planning of Flight Test Maneuvers ........................................................... 194
7.2.1 Flight Test Evaluation of a Transport Aircraft ............................... 196
7.2.2 Takeoff and Landing Tasks ............................................................ 196
7.2.2.1 Approach and Landing Task............................................. 196
7.2.2.2 Takeoff Task ..................................................................... 197
7.2.3 Other Maneuvers............................................................................. 198
7.3 Specific Flight Test Data Generation and Analysis Aspects ..................... 198
7.3.1 Longitudinal Axis Data Generation................................................ 199
7.3.2 LD Data Generation........................................................................ 201
7.4 Quality of Flight Test Maneuvers.............................................................. 201
7.5 Input Signals for Exciting Maneuvers ....................................................... 202
7.5.1 Design Consideration for Input Signals.......................................... 202
7.5.2 Specific Input Types ....................................................................... 204
7.6 Specific Maneuvers for Aerodynamic Modeling....................................... 204
7.6.1 Small Amplitude Maneuvers .......................................................... 204
7.6.1.1 Longitudinal Short-Period Maneuver................................ 205
7.6.1.2 Phugoid Maneuver ............................................................ 205
7.6.1.3 Thrust Input Maneuver...................................................... 205
7.6.1.4 Flaps Input Maneuver ....................................................... 205
7.6.1.5 LD Maneuvers................................................................... 206
7.6.1.6 Aileron Input Roll Maneuver............................................ 207
7.6.1.7 Rudder Input Maneuver .................................................... 208
7.6.1.8 DR Maneuver .................................................................... 208
7.6.1.9 Steady Heading Sideslip Maneuver .................................. 208
7.6.2 Large Amplitude Maneuvers .......................................................... 208
7.7 Specific Dynamic Maneuvers for Determination of Drag Polars.............. 211
7.7.1 Roller Coaster (Pullup=Pushover) Maneuver ................................. 213
7.7.2 SD Maneuver .................................................................................. 213
7.7.3 Acceleration and Deceleration Maneuver....................................... 213
7.7.4 WUT Maneuver .............................................................................. 214
7.8 Specific Maneuvers for Rotorcraft............................................................. 217
7.9 Flight Test Database Management ............................................................ 219
7.9.1 Basic Requirements ........................................................................ 220
7.9.2 Selection and Classification of Flight Data .................................... 220
7.9.2.1 Classification Based on Type of Maneuvers .................... 220
7.9.2.2 Classification Based on Flight Conditions........................ 221
7.9.2.3 Classification Based on Aircraft Configuration ................ 221
x
7.9.3 Data Storage and Organization....................................................... 221
7.9.4 Flight Test Database in Oracle ....................................................... 221
7.9.5 Brief Description of a Typical Program ......................................... 225
7.9.5.1 Transactions ...................................................................... 225
7.9.5.2 Graphs=Reports ................................................................. 225
7.9.5.3 User Maintenance.............................................................. 226
Epilogue ................................................................................................................ 226
Exercises ............................................................................................................... 226
References ............................................................................................................. 228
Chapter 8 Reconfiguration and Fuzzy Control Analysis ................................. 229
8.1 Introduction ................................................................................................ 229
8.2 Requirements of Flight Control ................................................................. 229
8.3 Stability=Control Augmentation Strategies................................................ 233
8.4 Performance Requirements and Criteria .................................................... 236
8.5 Procedure for the Design and Evaluation of Control Laws ...................... 236
8.6 Fuzzy Logic Control .................................................................................. 238
8.7 Fault Detection, Identification, and Isolation............................................. 246
8.7.1 Models for Faults ............................................................................ 246
8.8 Aircraft Reconfigurable=Restructurable Control System........................... 247
8.8.1 Sensor Fault Detection Scheme ...................................................... 250
8.8.2 Actuator Fault Detection Scheme................................................... 253
8.8.2.1 Reconfiguration Concept................................................... 254
8.8.3 Non-Model-Based Approach .......................................................... 256
Epilogue ................................................................................................................ 258
Exercises ............................................................................................................... 259
References ............................................................................................................. 260
Chapter 9 System Identification and Parameter Estimation............................. 263
9.1 Introduction ................................................................................................ 263
9.2 System Identification.................................................................................. 266
9.2.1 Time-Series=Regression Model Identification ................................ 266
9.2.2 Comparison of Several Model Order Criteria ................................ 268
9.2.3 Transfer Function Models from Real-Flight Data .......................... 271
9.2.4 Expert Systems for System Identification....................................... 272
9.3 Aircraft Parameter Estimation.................................................................... 272
9.3.1 Maneuvers, Measurements, and Mathematical Models.................. 273
9.3.2 Parameter-Estimation Methods ....................................................... 274
9.3.2.1 Equation Error Method ..................................................... 274
9.3.2.2 Maximum Likelihood=OEM............................................. 275
9.3.2.3 Filtering Methods .............................................................. 279
9.3.2.4 Parameter-Estimation Approaches for Inherently
Unstable=Augmented Aircraft ........................................... 282
xi
9.4 Determination of Stability and Control Derivatives
from Flight Data—Case Studies ................................................................ 283
9.4.1 Fighter Aircraft FA1 ....................................................................... 284
9.4.2 Fighter Aircraft FA2 ....................................................................... 285
9.4.3 Basic and Modified Transport Aircraft........................................... 285
9.4.4 Trainer Aircraft ............................................................................... 287
9.4.5 Light Canard Research Aircraft ...................................................... 288
9.4.6 Helicopter........................................................................................ 288
9.4.7 AGARD Standard Model ............................................................... 290
9.4.8 Dynamic Wind-Tunnel Experiments .............................................. 290
9.4.9 Iron Bird Results............................................................................. 291
9.5 Approaches for Determination of Drag Polars from Flight Data.............. 292
9.5.1 Model-Based Approach for Determination of Drag Polar ............. 293
9.5.2 Non-Model-Based Approach for Drag Polar Determination.......... 293
9.6 Analysis of Large Amplitude Maneuver Data........................................... 294
9.7 Global Nonlinear Analytical Modeling ..................................................... 296
9.8 ANN-Based Parameter Estimation ............................................................ 298
9.8.1 FFNN Scheme................................................................................. 299
9.8.2 RNN for Parameter Estimation....................................................... 300
9.9 Fuzzy Logic-Based Methods for Estimation ............................................. 303
9.9.1 ANFIS for Parameter Estimation.................................................... 303
9.9.2 Fuzzy Kalman Filter for State Estimation ...................................... 305
9.9.2.1 Tracking of Maneuvering Target ...................................... 309
9.10 Derivative-Free Kalman Filter for State Estimation .................................. 311
Epilogue ................................................................................................................ 317
Exercises ............................................................................................................... 317
References ............................................................................................................. 319
Chapter 10 Handling Qualities Analysis .......................................................... 323
10.1 Introduction .............................................................................................. 323
10.2 Pilot Opinion Rating ................................................................................ 323
10.3 Human Operator Modeling ...................................................................... 324
10.3.1 Motion Plus Visual and Only Visual Cue Experiments ............. 325
10.4 Handling Qualities Criteria ...................................................................... 328
10.4.1 Longitudinal HQ Criteria ............................................................ 329
10.4.1.1 Lower-Order Equivalent TF ........................................ 329
10.4.1.2 Control Anticipation Parameter ................................... 329
10.4.1.3 Bandwidth Criterion .................................................... 331
10.4.1.4 Neal–Smith Criterion ................................................... 331
10.4.1.5 Closed Loop Criterion ................................................. 332
10.4.1.6 Pitch Rate Response .................................................... 332
10.4.1.7 C* Criterion ................................................................. 332
10.4.1.8 Gibson’s Criteria .......................................................... 333
10.4.2 Lateral-Directional HQ Criteria .................................................. 334
10.4.2.1 Lower-Order Equivalent TF ........................................ 334
xii
10.4.2.2 Roll Angle–Sideslip Mode Ratio................................. 334
10.4.2.3 LD Modes.................................................................... 334
10.4.2.4 Roll Rate and Bank Angle Oscillations ...................... 335
10.4.2.5 Roll Performance ......................................................... 336
10.4.2.6 Sideslip Excursions...................................................... 337
10.5 Evaluation of HQ Criteria........................................................................ 337
10.5.1 HQ for Large Transport Aircraft................................................. 337
10.5.2 Rotorcraft Handling Qualities ..................................................... 338
10.5.3 Handling Qualities Analysis Tool............................................... 340
10.5.3.1 Hover and Low-Speed Requirements
(HLSR)—Pitch Axis Response Criteria ...................... 341
10.5.3.2 HLSR—Roll Axis Response Criteria .......................... 341
10.5.3.3 HLSR—Yaw Axis Response Criteria ......................... 343
10.5.3.4 HLSR—Heave Axis Response Criteria....................... 343
10.6 HQ Aspects for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles............................................ 343
10.7 Pilot–Aircraft Interactions........................................................................ 345
10.7.1 Longitudinal PIO Criteria ........................................................... 345
10.7.1.1 Ralph–Smith Criterion ................................................. 346
10.7.1.2 Smith–Geddes Criterion .............................................. 346
10.7.1.3 Phase Rate Criterion .................................................... 346
10.7.1.4 Loop Separation Parameter.......................................... 347
10.7.1.5 Neal–Smith Time-Domain Criterion ........................... 347
10.7.1.6 Bandwidth PIO Criterion............................................. 347
10.7.2 Lateral PIO Criteria..................................................................... 347
10.7.2.1 Ralph–Smith ................................................................ 348
10.7.2.2 Phase Rate.................................................................... 348
10.8 Model Order Reduction for Evaluations of HQ...................................... 348
Epilogue ................................................................................................................ 349
Exercises ............................................................................................................... 349
References ............................................................................................................. 350
Appendix A: Aerodynamics and Related Concepts ......................................... 353
Appendix B: Statistics and Probability ............................................................. 383
Appendix C: Signal and Systems Concepts ..................................................... 391
Bibliography ........................................................................................................ 407
Index..................................................................................................................... 409
专业书籍
下载地址:(回复后可见)
| ![]()